Newsletter Issue 13, 2012 |
|---|
Holter ECG from the Defibrillator in Non-Ischemic Cardiomyopathy Treatment Evaluation (DEFINITE) Study available in the THEW |
- Editorial: THEW ready to host Holter ECGs from Clinical trials: pioneering with the DEFINITE trial
- Regulatory Corner: CDRH joins the THEW initiative
- Regulatory Corner: Revamped HL7 aECG format
- Technical corner: THEW ECG viewer and algorithm library.
- The Delta50 method from Astra-Zeneca R&D.
Editorial: THEW ready to host Holter ECGs from Clinical trials: pioneering with the DEFINITE trial
by JP. Couderc, PhD, MBA
The purpose of the Defibrillator in Non-Ischemic Cardiomyopathy Treatment Evaluation (DEFINITE) Study was to determine if the combination of ICD therapy to optimal medical therapy reduces all-cause mortality in non-ischemic cardiomyopathy patients with low ejection fraction and NSVT/PVC's compared to optimal medical therapy only.
 The enrolled patients in this trial had a diagnosis of nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy, LVEF < 36%, and PVC's or unsustained ventricular tachycardia. The control group received standard medical therapy, while the test-ICD group received standard medical therapy and a single-chamber ICD. At 2 years, the mortality rate was greater in the control group (14.1%) than the test-ICD group (7.9%). There were significantly more sudden deaths from arrhythmia in the control group than there were in the test-ICD group (p=0,006). The investigators concluded that the combination of ICD therapy with standard optimal medical therapy reduced the risk of sudden death from arrhythmia in patients with severe non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy.
The enrolled patients in this trial had a diagnosis of nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy, LVEF < 36%, and PVC's or unsustained ventricular tachycardia. The control group received standard medical therapy, while the test-ICD group received standard medical therapy and a single-chamber ICD. At 2 years, the mortality rate was greater in the control group (14.1%) than the test-ICD group (7.9%). There were significantly more sudden deaths from arrhythmia in the control group than there were in the test-ICD group (p=0,006). The investigators concluded that the combination of ICD therapy with standard optimal medical therapy reduced the risk of sudden death from arrhythmia in patients with severe non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy.
We are glad to announce that the Holter ECG recordings acquired in this trial are now hosted in the THEW and are available for research to our members. Two hundred and thirty six patients were enrolled in this study and got a Holter ECG recording acquired either at enrollment of later during the trial. The patients were followed for 29 months in average. The enrollment criteria included LVEF<36%, the presence of ambient arrhythmias, a history of symptomatic heart failure, and the presence of non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. Ambient arrhythmias were defined by an episode of non-sustained ventricular tachycardia on Holter (3 to 15 beats at heart rate superior to 120 beats per minutes) (not the ECGs hosted in this database). The acquisition of the Holter recordings (hosted in the THEW) was initiated after the start of the trial. ECGs were acquired at baseline or at the next scheduled follow-up visit for patients who were already enrolled in the study. This data represents a unique opportunity to test ECG markers for risk of arrhythmic death in a group of patients with a documented cardiac history and valuable followup information.
The database consists of 401 24-hour Holter recordings recorded in 236 patients. One hundered and forty recordings were acquired at baseline, and the remaining were acquired during followup visit. More information about the database can be found on the database webpage of the THEW website. Importantly, we have designed a new type of research agreement with Northwestern University (Chicago, IL) in order to enable the distribution of the DEFINITE data to the Scientific community. A review committee consisting of individuals from the THEW and from the group which conducted the DEFINITE trial has been formed. Prof. A. Kadish and his collaborators will join the THEW review committee to review research proposals and ensure that any proposed scientific investigation can benefit from their experience with the data. The official release date of this new database from our repository is March 1st, 2012. More information can be found here .
It is noteworthy that this new type of data sharing agreement represents a cornerstone for our intiative. We have built through this effort a legal platform welcoming data from large clinical trials while ensuring that principal investigators will remain involved in supporting the research activities of our members. We hope that this strategy will lead other Institutions that have conducted ground-breaking clinical research to join our endeavor.
In addition, we welcomed during this past quarter several new members. First, large ECG equipment companies such as Philips Healthcare and Samsung Electronic purchased the full access to our database. Second, the Center for Devices and Radiological Health has joined us as well. Finally, we present in this issue the work from Astra-Zeneca related to novel ECG markers to quantify the variability fo the T-wave. The technique was evaluated on data from the THEW as well, and the result of this investigation will be presented during the annual congress of the European Cardiac Arrhythmia Society in Munich this upcoming April.
All the THEW team hopes you will enjoy this long-expected new issue of our Newsletter, and wish you, with a bit of delay but a warm feeling, a Happy and Successful New Year 2012.

FDA: New Legal FDA-THEW Data Use Agreement, the FDA-CDRH joined the THEW initiative
THEW continues to feed the research activities at the FDA with ECG data. In May last year, the National Center for Toxicological Research (NCTR) gained access to several database from the THEW triggering the first official research project based on THEW data conducted at FDA. In this process, the agency released a new Data Use Agreement specifically designed for FDA employees. The document is available for download here . This past month, the Center for Devices and Radiological Health registered with THEW through this new legal agreement that will facilitate the access of the THEW data to FDA employees for research purposes. Dr. David Strauss, scientist and medical officer at FDA's Center for Devices and Radiological Health, working on differentiation of benign from malignant QT prolongation commented, "The THEW collection of databases is a tremendous resource for the research community, and access to the databases will help FDA perform regulatory science."
The FDA will held a public meeting on Wednesday, March 14, 2012, from 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. at the FDA's White Oak Campus to discuss the new HL7 Annotated ECG data format developed to handle long-term ECG data from continuous recordings. This change was planned in order “to expand both the hardware and the software resources of the FDA's ECG Warehouse. FDA is interested in the perspective of manufacturers, ECG laboratories, investigators, industry, and academic researchers as it seeks to improve the collection, analysis, submission, and review of continuous ECG recordings for purposes of assessing drug safety”.
During this meeting, Mortara Instrument will describe several new analytic features of the FDA warehouse and the proposed modifications of the current HL7 aECG format in order to handle continuous ECG recordings and their associated beat annotation information. Barry Brown, Product Integration Manager at Mortara Instrument, commented: “The current HL7 aECG format is unpractical for storing large amount of information such as the ones available in 24-hour Holter recordings. For instance, a continuous 48-hour 12-lead recording (recorded with high resolution i.e. 1 sample every millisecond) could require up to 10 GB of storage space. Thus, Mortara Instrument will propose to insert links to binary files inside the HL7 aECG file to efficiently store and access these information.“
This new feature will be possible by inserting XML tags describing the attributes of the binary file (binary structures, signal data organization, etc.) in the current HL7 aECG structure. Such solution seems very attracting since it provides flexibility to ECG device companies to fit in their existing format. The ISHNE format used in the THEW is one of them. Interestingly, the format will also ensure that standard compression schemes could be used.
Today, various computerized tools are available to measure beat-to-beat intervals from continuous ECG signals (i.e. P onset , QRS onset, T-wave end, etc.). The storage of these measures in 100,000 to 150,000 cardiac beats per 24-hour makes the current XML HL7 aECG format very unpractical. So, Mortara Instrument will propose to insert a second link to an annotation file in binary format. The structure of this file will be flexible as well, it has been described by Barry Brown as a file containing "the beat number in each row and a list of fiducial points stored in each column with no limitation on the number of columns".
The revamping of the HL7 aECG have been wisely crafted by Mortara Instrument team in collaboration with regulators. The discussions that will occur in March are going to be interesting. Ultimately they should lead to improve the analysis of ECG acquired in drug safety studies by providing the ability to regulators and other stakeholders to better assess the confounding effects of a large spectrum of factors on ECG markers used in drug safety.
Official FDA notice for the public meeting is available for download here
TECHNICAL CORNER: THEW ECG viewer and algorithm library
All the ECG data currently hosted in the repository are stored using a single type of format: the ISHNE format. This format is described in our website. To facilitate the access to the raw signals, we have opened a library of codes to read these signals and annotation information. These procedures are available for download in our webiste in order to facilitate anyone with a minimum of coding experience to integrate this code into their development platform. As of today, c++ and MATLAB codes are provided, and we planned to regularly update tools in a common interest of facilitating the access and analysis of the data from our repository.
EXPERT OPINIONS: the Delta-50 method.
By Christina Abrahamsson PhD, Corina Dota MD, Bo Skallefell BSc, Leif Carlsson PhD, Nils Edvardsson MD PhD, Göran Duker PhD, AstraZeneca R&D, Göteborg, Sweden.
Increased beat-to-beat variability in cardiac repolarization time is a tentative risk marker of drug-induced torsades de pointes. Evaluation of its value as a risk marker requires automatic measurements of the repolarization time on single beats, which is truly a challenge, especially when the ECG signal is noisy or of low amplitude. The deltaT50 method measures the beat-to-beat variability of the “T50-interval”, the time from the intersection of the RS line and the isoelectric line to 50% of the T wave downslope (Fig. 1). Noise reduction of the T wave downslope is achieved by using 21 points smoothing (Fig 2). The deltaT50 algorithm is incorporated in a special version of EClysis used for research properties. It enables automatic, operator-independent measurements on ECG signals with a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of at least 10 if beats following changes in the RR interval exceeding 150 ms are excluded and if 9 beat pairs are available for analysis.
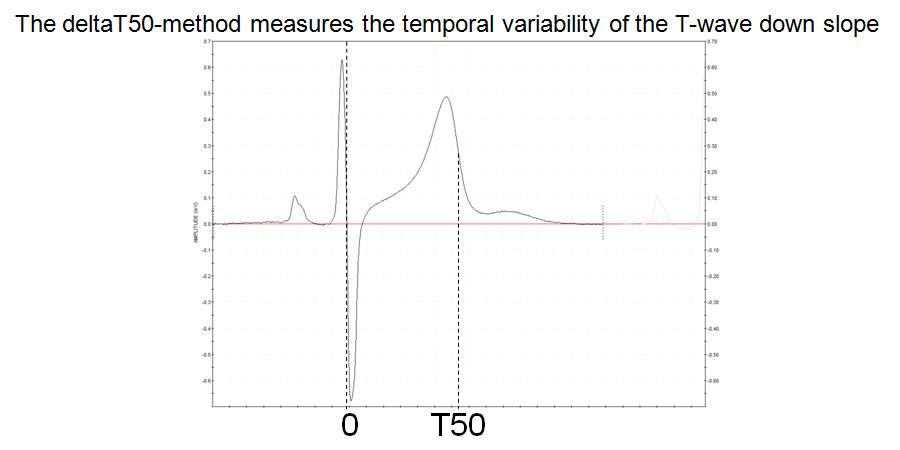
FIGURE 1:
Figure 1 The deltaT50 method measures the beat-to-beat change in the “T50 interval”, i.e. from the intercept between the RS and isoelectric lines to 50% of the T wave downslope
The reason for choosing the start of the T50 interval at the intersection of the RS and isoelectric lines was that this point is easier to determine automatically than the start of the QRS complex. The idea of measuring the interval, not to the end of the T wave (which is also very difficult to define), but to 50% of the T wave downslope, arose from what can be seen on superimposed, consecutive ECG complexes, namely that the whole T wave downslope appears to shift in parallel when the QT interval changes beat by beat. This was also confirmed from measurements of the variability at 20 and 80% of the T wave downslope. However, deltaT50 was chosen as the primary variable, since tentative errors in the estimation of the maximum and minimum of the T wave downslope, which may occur due to noise, have a smaller effect on the interval at the steep 50% level than at the flatter 20 and 80% levels.
A study in 10 young, healthy subjects was initially undertaken to establish the proper conditions for the measurements of deltaT50, i.e. to investigate the effect of smoothing, the effect of added noise to the ECG signal, the relationship between changes in the RR and T50 intervals and the least number of beats for a reliable estimation of deltaT50. Recordings from another 32 subjects, 18 to 68 years old, were included to investigate whether measurements of deltaT50 should be corrected for age, heart rate (HR), T wave amplitude, heart rate variability (deltaRR) or QTcF.
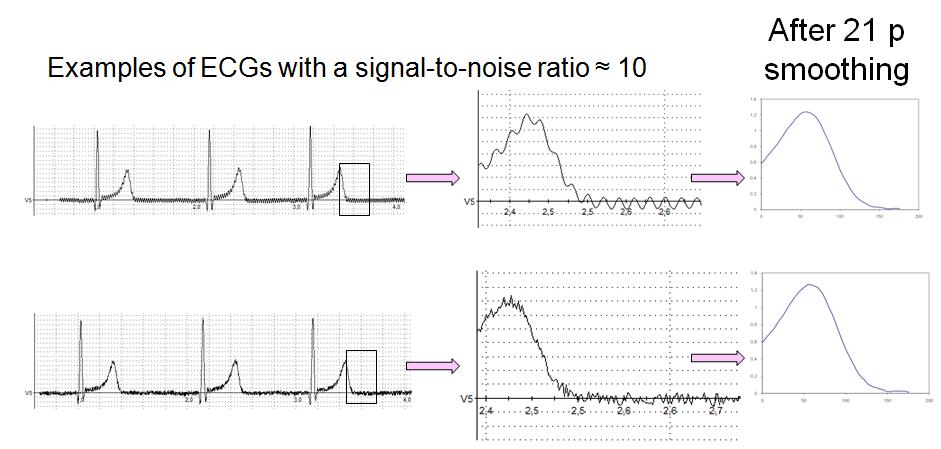
FIGURE 2:
Figure 2. The effect of noise and smoothing on deltaT50 was studied by adding noise of increasing amplitude to noise-free ECG signals. In these examples, sinusoidal (upper panel) or white noise (lower panel) was added, resulting in a signal-to-noise ratio of approximately 10 and a substantial increase in deltaT50. However, both the appearance of the ECGs and deltaT50 were normalized after 21 points of smoothing.
Smoothing is an efficient tool to iron out wrinkles on the ECG signal (Fig. 2). We started by investigating the effect of smoothing on noise-free signals and found that not even 21 points smoothing significantly altered deltaT50. When sigmoidal or white noise was added to the signals, deltaT50 increased in proportion to the amplitude of the added noise. However, 21 points smoothing restored the shape of the signal (Fig 2), and deltaT50 could be measured with high precision on signals with a SNR before smoothing of at least 10.
The beat-to-beat changes in the T50 interval were very small in the healthy subjects, on average 1.5 ms, but, as expected, large changes in the RR interval resulted in larger changes in the T50 interval (Fig 3A). To avoid the effect of these large changes in RR, which were only seen in the subjects with pronounced sinus arrhythmia, we decided to exclude all beat pairs where RR changed more than 150 ms (Fig 3B). This reduced the variability in deltaT50 both between and within the subjects, and a reliable estimation of deltaT50 could be done on only 9 beat pairs. We found no correlation between deltaT50 and age, gender, T wave amplitude, SNR or QTcF, but significant correlations to both HR and deltaRR. However, differences in HR and deltaRR explained only 2.6 and 3.5%, respectively, of the within subject variability, and only 10 and 19%, respectively, of the variability in deltaT50 between subjects. We therefore decided to measure deltaT50 without correction for any of these tentatively confounding factors.
The average deltaT50 was 1.5±0.41 ms in the 42 subjects, ranging from 0.86 to 2.84 ms, and correlated well between repeated measurements in the same subject.
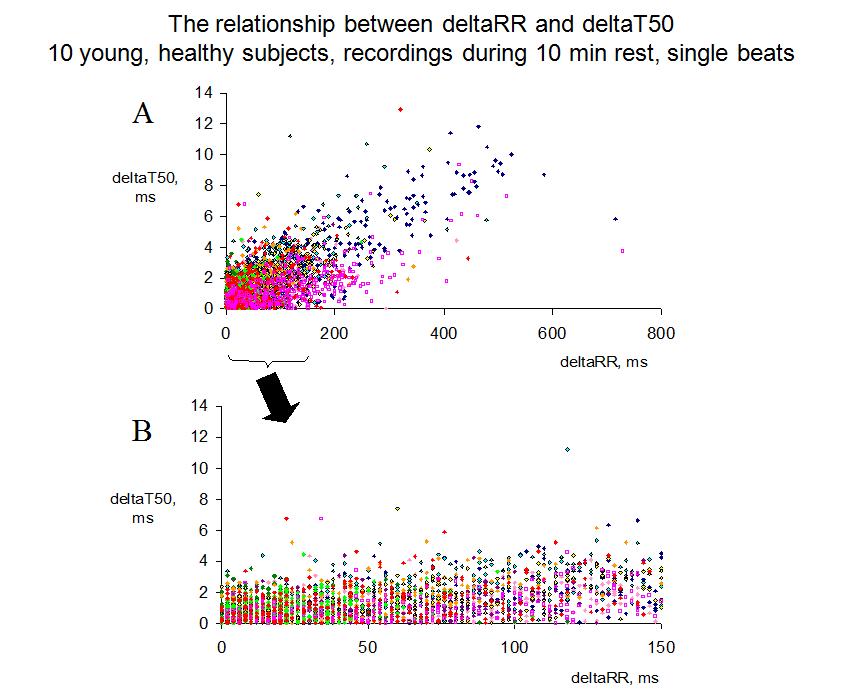
FIGURE 3:
Figure 3. Panel A shows the beat-to-beat changes in the T50 interval (deltaT50) versus the change in the preceding RR interval (deltaRR) for all single beats recorded during 10 min of rest in 10 young, healthy subjects (one symbol/subject). With the deltaT50 method, all beats following a change in the RR interval of more than 150 ms are excluded, since not all subjects display this large RR variability, and, if so, only occasionally. When deltaRR ranged between 0 and 150 ms, deltaT50 seldom exceeded 4 ms (Panel B), and the average deltaT50 was 1.5 ms in this interval.
To summarize, the deltaT50 method can be used to measure beat-to-beat variability in cardiac repolarization time without corrections for age, gender, T wave amplitude, SNR, HR, deltaRR or QTcF.
- after 21 points smoothing of
- at least 9 pairs of ECG complexes with positive T waves and
- with a SNR of at least 10
- during changes in the RR interval between ± 150 ms.
The paper describing the method was recently published in Journal of Electrocardiology (please click here ).
Since AstraZeneca joined the THEW initiative last year, the deltaT50 method has been applied to the Holter ECGs from the healthy volunteers and the patients with Long QT Syndrome. The THEW data will be used for further validation of the technology and to strengthen the link between increased repolarization variability and arrhythmia risk.